Is your computer suddenly running slower than usual? Do your fans sound like a jet engine taking off? If you've checked Task Manager and seen "Antimalware Service Executable" consuming massive amounts of memory, you're facing a common Windows issue. This "antimalware service executable high memory usage" problem can cripple your system's performance, making even simple tasks frustratingly slow.

Understanding the Antimalware Service Executable
This process (MsMpEng.exe) is the backbone of Windows Defender, Microsoft's built-in security solution. It constantly scans your system for threats like:
Viruses
Spyware
Ransomware
Other malware
While essential for protection, it sometimes goes overboard, causing "antimalware service executable high memory" and disk usage issues that can freeze your entire system.
What Causes Antimalware Service Executable High Memory?
1. Scheduled Scans Running
Windows Defender performs automatic scans that can consume:
70-90% of your CPU
Several GB of RAM
Constant disk activity
These typically occur during low-usage periods, but sometimes trigger at inconvenient times.
2. Real-Time Protection Overworking
The real-time scanner might be:
Checking every file you access
Scanning emails unnecessarily
Over-analyzing safe programs
3. Outdated System Components
Old Windows Defender definitions or corrupted system files can cause efficiency problems leading to "antimalware service executable high disk" usage.
4. Software Conflicts
Other security tools like McAfee or Norton often clash with Windows Defender, creating resource battles.
5. Malware Fighting Back
Some sophisticated viruses intentionally stress your antivirus to hide their activities.
Fixes That Work for Antimalware Service Executable High Memory
Temporary Solution: Restart the Service
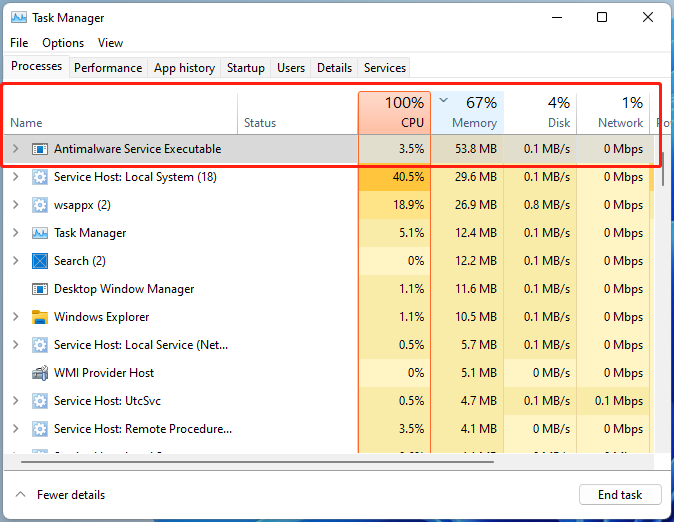
Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc)
Find "Antimalware Service Executable"
Right-click and select "End task"
It will restart automatically with fresh resources
Permanent Solutions:
Adjust Windows Defender Scans
Open Windows Security
Go to Virus & threat protection
Click "Manage settings" under Virus & threat protection settings
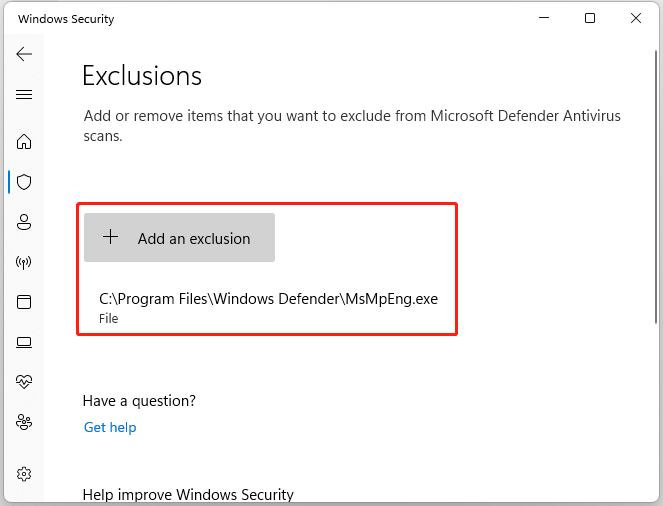
Turn off "Cloud-delivered protection" temporarily
Under "Exclusions," add folders you trust
Schedule Scans for Off-Hours
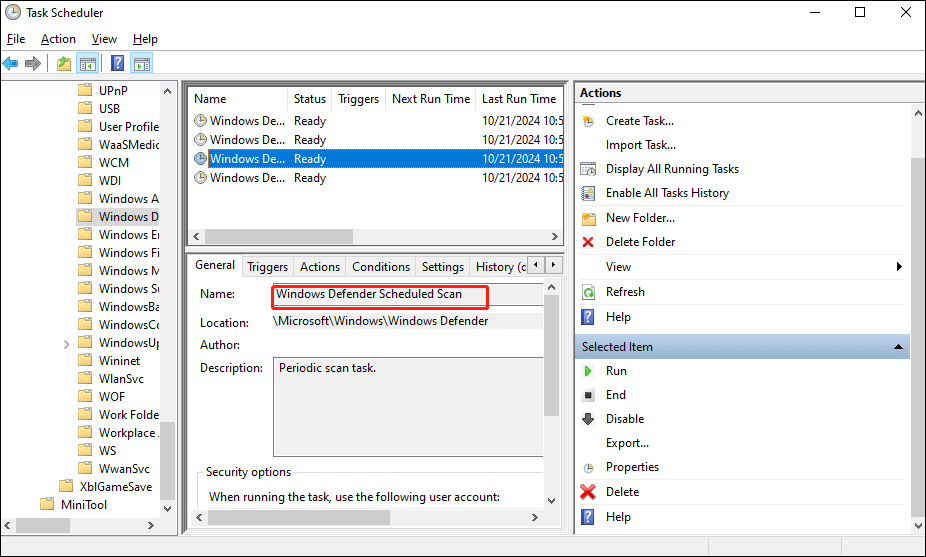
Open Task Scheduler
Navigate to: Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender
Modify "Windows Defender Scheduled Scan" properties
Set it to run when you're not using the PC
Update Your System
Outdated drivers are a common culprit behind issues such as "antimalware service executable high memory usage." These outdated drivers can cause inefficiencies in how your hardware communicates with your system's security software, like Windows Defender, leading to increased memory usage and potential performance bottlenecks.
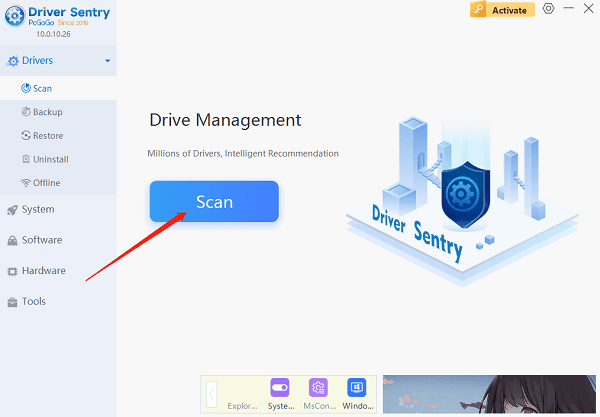
To address this, we recommend using PcGoGo Driver Sentry, a powerful tool that simplifies the process of updating your drivers. Here’s how you can use it to keep your system running smoothly:
Download and Install: Visit pcgogo.com to download the latest version of PcGoGo Driver Sentry. Adhere to the installation guidelines to install it on your computer.
Run a Full System Scan: Once installed, launch the application and run a full system scan. This scan will identify all outdated or missing drivers on your system.
Update All Flagged Drivers with One Click: After the scan is complete, PcGoGo Driver Sentry will present a list of drivers that need updating. You can update all flagged drivers with just one click, ensuring that your hardware is running on the latest and most compatible drivers.
Schedule Automatic Weekly Scans: To maintain optimal system performance, set up automatic weekly scans. This ensures that your drivers are always up-to-date without requiring manual intervention.
By keeping your drivers updated, you ensure that your hardware communicates efficiently with Windows Defender and other system components. This not only prevents unnecessary resource drains but also enhances overall system stability and performance. Regular updates are crucial in maintaining a secure and efficient computing environment.
Disable Windows Defender (Temporarily)
For emergency situations when you need full performance:
Open Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc)
Navigate to: Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Enable "Turn off Microsoft Defender Antivirus"
Remember to re-enable protection later!
Switch to Third-Party Antivirus
If problems persist, consider alternatives like:
Bitdefender
Kaspersky
Malwarebytes
These often have lighter resource footprints than Windows Defender.
Advanced Troubleshooting
For persistent "antimalware service executable high disk" issues:
Check for Malware
Sometimes the scanner is working hard because it's actually fighting something:
Run an offline Windows Defender scan
Use the Malicious Software Removal Tool
Try a second-opinion scanner like HitmanPro
Clean Boot Your System
Type "msconfig" in Run dialog
Go to Services tab
Check "Hide all Microsoft services"
Disable all remaining services
Restart and check if problem persists
Monitor with Process Explorer
Microsoft's advanced Task Manager replacement shows exactly what files Defender is scanning.

When All Else Fails
If you've tried everything and still face "antimalware service executable high memory" problems:
Reset Windows Defender
Run these commands in Admin Command Prompt:
mpcmdrun.exe -removedefinitions -all
mpcmdrun.exe -resetplatform
Consider Hardware Upgrades
Add more RAM (16GB is ideal for modern Windows)
Switch to an SSD if using a hard drive
Make sure there is adequate cooling to avoid thermal throttling
Perform a Windows Repair Install
Keeps your files while refreshing system components.
Keep Your System Running Smoothly
Regular maintenance prevents most "antimalware service executable high memory usage" issues:
Run PcGoGo Driver Sentry weekly to keep drivers updated
Clean temporary files monthly
Defragment HDDs (not needed for SSDs)
Monitor startup programs
Remember - while the Antimalware Service Executable can be annoying when it misbehaves, it's also your first line of defense against real threats. Finding the right balance between security and performance is key to a frustration-free computing experience.