
Network connection problems on Windows are often caused by corrupted, missing, or outdated network adapter drivers. If your computer cannot connect to WiFi or Ethernet, reinstalling the network adapter driver is one of the most effective solutions.
This guide explains how to reinstall a network adapter driver properly, starting with the fastest and safest method using Driver Sentry, followed by several manual troubleshooting options.
Update Network Adapter Drivers Using Driver Sentry
Before attempting manual fixes, it is strongly recommended to use a professional driver management tool. Driver Sentry automatically detects faulty or outdated network drivers and installs the correct versions for your system, reducing the risk of compatibility issues.
Download and Install:
Use a temporary internet connection (Ethernet or a mobile phone USB tether) if your PC is completely offline.
Download and install the Driver Sentry application onto your Windows PC.
Run Scan:
Launch Driver Sentry from the desktop or Start Menu, click the "Scan" button.
The software will perform a deep analysis of your system, focusing on network, Ethernet adapters and core system components.
Execute Update:
The results will show you a list of all drivers that need attention. Select the necessary drivers and click the "Upgrade" or "Repair Now" button.
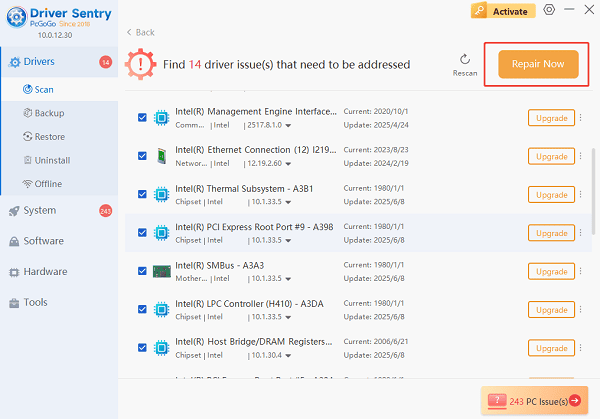
Driver Sentry will download the latest, certified versions specific to your WiFi adapter, crucial for reliable scanning and connection establishment.
Restart Your PC:
Do not interrupt the process. Once finished, restart your computer to apply the changes.
Using Driver Sentry ensures that the correct driver version is installed without manual searching, which is especially helpful if Windows cannot access the internet.
Method 1: Reinstall Network Adapter via Device Manager
If you prefer a manual approach, Windows Device Manager allows you to uninstall and reinstall network adapter drivers.
Steps to Reinstall Network Adapter Driver Manually:
Press Windows + X and select Device Manager.
Expand the "Network adapters" section, right-click your WiFi or Ethernet adapter and choose "Uninstall device".
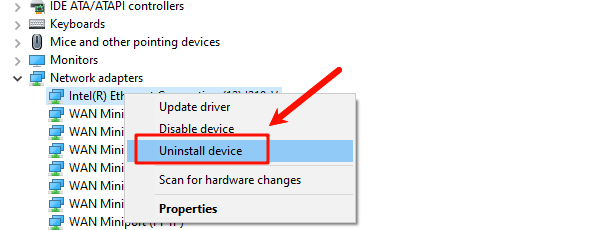
Check the option "Delete the driver software for this device" if available.
Click "Uninstall" and wait for the process to finish.
Restart your computer.
After rebooting, Windows will attempt to reinstall the default network adapter driver automatically.
Method 2: Install Network Adapter from Manufacturer Website
If Windows fails to reinstall the driver correctly, downloading it directly from the hardware manufacturer is another effective solution.
How to Install the Driver Manually:
Identify your network adapter model: Use Device Manager or check your laptop or motherboard specifications.
Visit the official manufacturer website: Common manufacturers include Intel, Realtek, Broadcom, ASUS, Dell, HP, and Lenovo.
Download the correct driver for your Windows version: Ensure the driver matches your system architecture (64-bit or 32-bit).
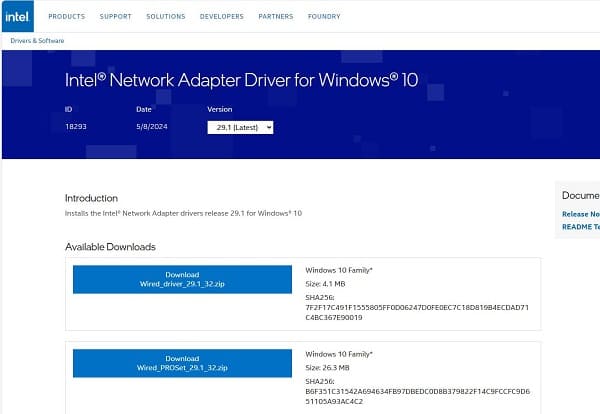
Run the installer and follow on-screen instructions.
Restart your PC after installation.
Method 3: Use Windows Network Reset
If driver reinstallation does not solve the issue, a network reset can clear corrupted configurations.
Steps to Reset Network Settings:
Open Settings and go to "Network & Internet".
Scroll down and select "Network reset".
Click "Reset now" and confirm.
Restart your computer.
This process reinstalls network adapters and resets all network-related settings.
Common Causes of Network Adapter Driver Issues
Outdated or incompatible drivers
Corrupted driver files after Windows updates
Incorrect driver installation
Malware or system file damage
Power interruptions during driver updates
Understanding these causes helps prevent recurring network problems.
Final Thoughts
Reinstalling a network adapter driver is a proven way to fix WiFi and Ethernet connection issues on Windows. Using Driver Sentry provides the fastest and most reliable solution by automatically detecting and reinstalling the correct drivers. If necessary, manual methods such as Device Manager, manufacturer downloads, and network resets offer additional ways to restore connectivity.\