
The frustrating message "Connected, no internet access" or "No internet, secured" is one of the most common yet confusing problems faced by Windows users. It means your PC is successfully linked to your router (WiFi signal is good), but the router itself isn't passing data from the wider internet to your PC.
The cause can range from a simple DNS failure to complex driver conflicts or IP configuration issues. This comprehensive guide provides systematic, step-by-step methods to diagnose and fix this connectivity roadblock.
1. The First Step: Eliminate Driver Conflicts and Instability
The underlying stability of your internet connection relies entirely on your Network Adapter Drivers (WiFi/Ethernet) and your Chipset Drivers. Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible network drivers are the most frequent cause of intermittent connectivity issues where the PC cannot correctly interpret the internet data stream from the router.
Driver Sentry is an efficient tool that performs a deep scan of your entire system, identifies missing or outdated drivers, and installs the correct, stable versions, ensuring your network adapter and related hardware are functioning flawlessly.
Download and Install:
Click the "Download" button to download the software package.
Install it on your Windows PC.
Scan Your System:
Launch the application. Click "Scan".
Driver Sentry will automatically perform a thorough scan, focusing specifically on your Network Adapter Driver (WiFi/Ethernet) and your Chipset Drivers.
One-Click Update:
The results will show you a list of all drivers that need attention. Simply click the "Repair Now" button.
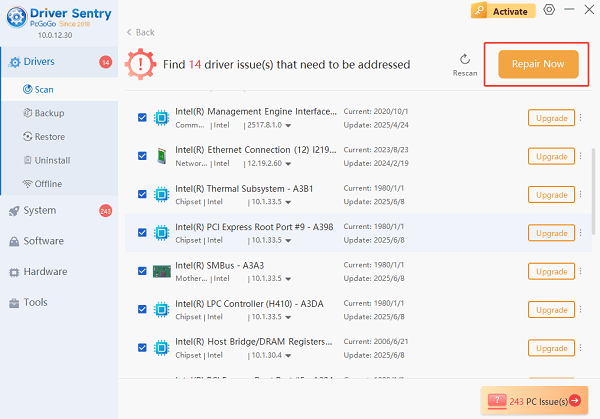
The tool will download and install the correct, verified versions of every driver at once.
Restart Your PC:
Once the installation is finished, it's crucial to restart your computer to integrate the new drivers fully.
2. Router and Network Configuration Fixes
If drivers are stable, the problem is likely an issue with the local network setup or cached data.
The Universal Fix (Power Cycle):
The simplest fix often resolves the most stubborn issues by clearing the IP and DNS cache on both your PC and router.
Shut Down PC: Completely shut down your computer.
Power Off Router/Modem: Unplug both your router (the device broadcasting the WiFi signal) and your modem (the device connected to your ISP line, if separate) from the wall power.
Wait: Wait a full 60 seconds. This ensures all residual memory and cached connections are cleared.
Power On: Plug the modem back in and wait until its lights stabilize (usually 1-2 minutes). Then, plug the router back in and wait for it to stabilize.

Restart PC: Turn on your PC and test the connection.
Flush DNS and Reset IP Stack:
This step forces your PC to discard old, faulty network configuration data and request a fresh, clean connection from the router.
1). Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Click the Start button, type "cmd", right-click on "Command Prompt", and select "Run as administrator".
2). Enter Commands Sequentially: Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each one:
ipconfig /release
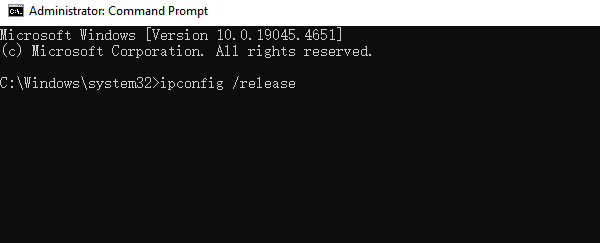
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /renew
netsh winsock reset
3). Restart: Restart your computer after running all four commands.
3. Advanced Network Settings Fixes
If the basic troubleshooting fails, you may need to look at the network adapter settings.
Use Google's Public DNS:
Your ISP's default DNS server might be down or routing slowly. Switching to a public DNS can often restore connectivity.
1). Open Network Connections: Press Windows Key + R, type "ncpa.cpl", and press Enter.
2). Access Properties: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Properties".
3). Edit Protocol: Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties".
4). Use Custom DNS: Select "Use the following DNS server addresses" and enter Google's public DNS:
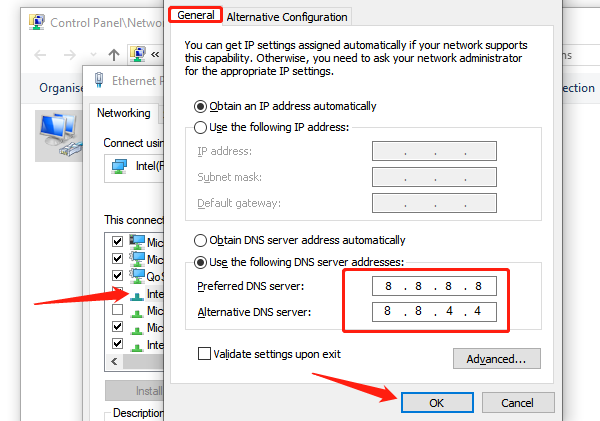
Preferred DNS server: 8.8.8.8
Alternate DNS server: 8.8.4.4
5). Save and Test: Click "OK" on both windows and test your internet connection.
Reset Windows Network Stack:
This performs an aggressive reset of all network components, similar to a factory reset for your network settings.
Open Settings: Press Windows Key + I to open the Settings app.
Navigate to Network Reset: Go to "Network & Internet" settings, scroll down, and click "Network reset".
Perform Reset: Click "Reset now". You will be warned that your PC will restart in 5 minutes.
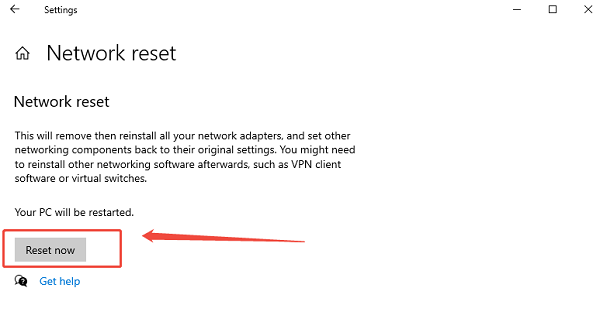
Reconnect: After the restart, you will need to re-enter your WiFi password.
Conclusion
The "Connected, no internet access" error is a common but fixable issue that often boils down to a communication error. By prioritizing system stability and ensuring all network drivers are up-to-date with Driver Sentry, then methodically using the Power Cycle, DNS Flush, and Network Reset solutions, you can reliably restore your internet connection and regain full online access.