
Seeing a WiFi connection but having no internet access on Windows is one of the most common and frustrating network problems. Your laptop or desktop may show "Connected, no internet", web pages fail to load, and apps cannot go online. This issue is usually related to outdated or faulty network drivers, incorrect network settings, DNS conflicts, or router and ISP problems.
This guide provides a complete troubleshooting walkthrough. We start with updating drivers using Driver Sentry, as driver issues are the most frequent cause. Then we cover multiple proven fixes so you can restore a stable internet connection.
Update Network Drivers First Using Driver Sentry
Outdated, missing, or incompatible WiFi drivers are the primary reason Windows connects to a network but cannot access the internet. Updating drivers early saves time and avoids unnecessary system changes.
Download and Install:
Use a temporary internet connection (Ethernet or a mobile phone USB tether) if your PC is completely offline.
Download and install the Driver Sentry application onto your Windows PC.
Run Scan:
Launch Driver Sentry from the desktop or Start Menu, click the "Scan" button.
The software will perform a deep analysis of your system, focusing on network and core system components.

Execute Update:
The results will show you a list of all drivers that need attention. Select the necessary drivers and click the "Upgrade" or "Repair Now" button.
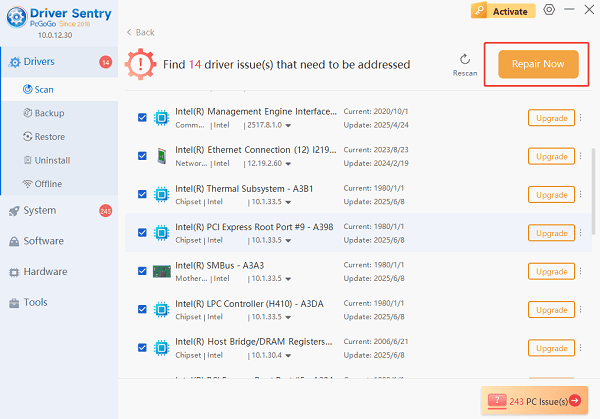
Driver Sentry will download the latest, certified versions specific to your WiFi adapter, crucial for reliable scanning and connection establishment.
Restart Your PC:
Restart your computer to apply the changes.
After rebooting, reconnect to your WiFi network and check if internet access is restored.
Why this works:
Ensures compatibility with recent Windows updates
Fixes corrupted driver files
Resolves hidden conflicts between network adapters and the OS
Common Causes of "WiFi Connected but No Internet"
Understanding the cause helps you apply the correct fix:
Outdated or incompatible WiFi drivers
Incorrect IP or DNS configuration
Router or modem firmware issues
ISP service interruptions
VPN or firewall conflicts
Corrupted Windows network components
Fix 1: Restart Router, Modem, and PC
This simple step often resolves temporary network conflicts.
Turn off your PC.
Unplug the router and modem from power.
Wait at least 60 seconds.
Plug the modem back in first and wait until all lights stabilize.
Plug in the router and wait again.

Turn on your PC and reconnect to WiFi.
If other devices also have no internet, the issue is likely with the router or ISP.
Fix 2: Run Windows Network Troubleshooter
Windows includes a built-in tool that can automatically fix common issues.
Press Windows + I to open Settings.
Go to "Network & Internet", select "Status".
Find "Network Adapter" and run the troubleshooter.
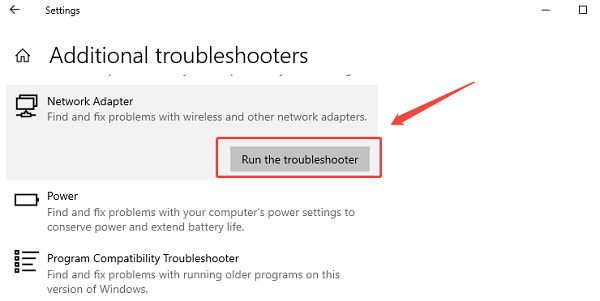
Follow the on-screen instructions.
This tool can reset adapters, fix configuration errors, and detect gateway problems.
Fix 3: Reset TCP/IP and Network Configuration
Corrupted network settings can block internet access even when WiFi is connected.
1. Type "cmd" in Windows Search.
2. Right-click Command Prompt and choose "Run as administrator".
3. Enter the following commands one by one, pressing Enter after each:
netsh winsock reset
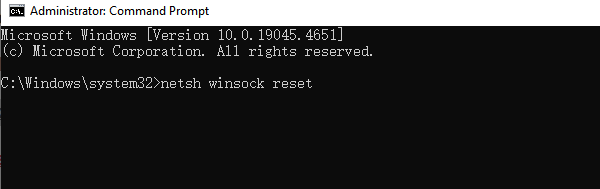
netsh int ip reset
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /flushdns
4. Restart your computer.
This resets core networking components and refreshes your IP address.
Fix 4: Change DNS Server Settings
Faulty DNS servers can prevent websites from loading.
1. Press Windows + R, type "ncpa.cpl", and press Enter.
2. Right-click your active WiFi adapter and select "Properties".
3. Double-click "Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4)".
4. Select Use the following DNS server addresses. Enter:
Preferred DNS server: 8.8.8.8
Alternate DNS server: 8.8.4.4
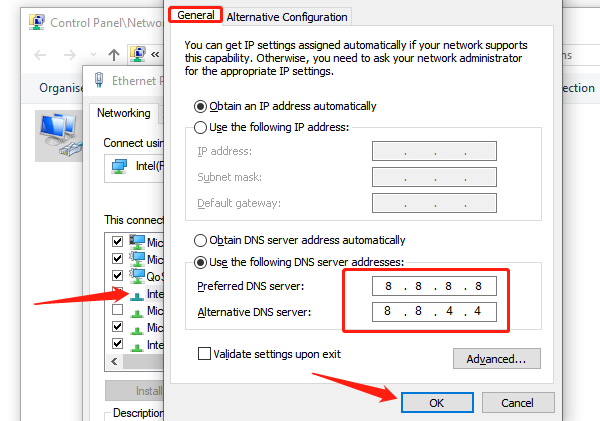
5. Click OK and reconnect to WiFi.
Fix 5: Disable Firewall or Security Software Temporarily
Some VPNs or firewalls block network traffic.
Disconnect any active VPN.
Temporarily disable third-party firewall or security software.
Test your internet connection.
If the internet works, reconfigure or update the conflicting software.
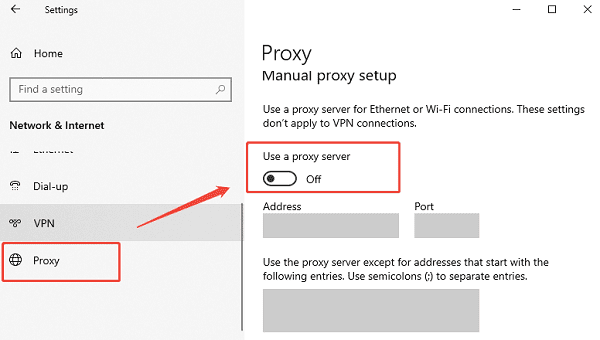
Fix 6: Check Proxy Settings
Incorrect proxy settings can prevent internet access.
Open Settings.
Go to Network & Internet > Proxy.
Turn off "Use a proxy server" unless required by your network.
Restart your browser and test the connection.
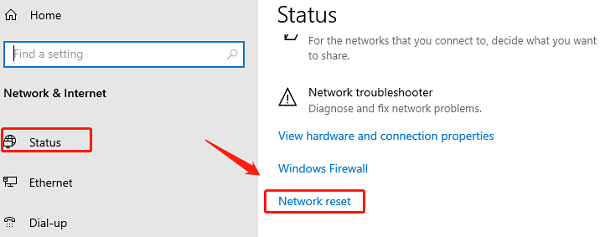
Fix 7: Reset Network Settings in Windows
If all else fails, a full network reset can help.
Open Settings.
Go to Network & Internet > Advanced network settings.
Select "Network reset".
Click "Reset now".
Restart your PC and reconnect to WiFi.
Note: This removes saved WiFi networks and VPN settings.
When to Contact Your ISP
If:
Multiple devices show WiFi connected but no internet.
Router lights indicate no WAN or internet signal.
The problem persists after all fixes.
Contact your internet service provider to check for outages or line issues.
Conclusion
"WiFi connected but no internet" on Windows is usually caused by driver problems or misconfigured network settings. Updating your network drivers with Driver Sentry should always be the first step, as it resolves most cases quickly and safely. If needed, follow the additional fixes in this guide to fully restore internet access. Keeping drivers up to date and network settings clean is the key to stable and reliable WiFi connectivity on Windows.