
Experiencing a sudden loss of sound on your computer can be frustrating. A silent system is typically caused by issues ranging from simple volume mistakes and hardware connection errors to complex driver conflicts or disabled Windows services.
To quickly restore your audio, this guide provides a systematic, step-by-step approach to troubleshooting the most common causes, starting with the foundation of all sound output: your audio drivers.
Part I: Driver and Software Integrity
Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible audio drivers are the single most frequent cause of sound failure on Windows PCs.
Method 1: Automated Driver Update with Driver Sentry
Manually troubleshooting and updating integrated audio drivers (like Realtek, Intel HD Audio, or Creative) can be complex and requires navigating the Device Manager. A specialized utility automates this process, ensuring all necessary audio and system drivers are perfectly stable.
Download and Install:
Click the "Download" button to download the software package.
Install it on your computer.
Run Scan:
Launch the application and click the "Scan" button.
The software will perform a deep analysis of your system, focusing on your audio devices and critical motherboard components.
Install the Update:
The results will show you a list of all drivers that need attention. Select the necessary audio drivers and click the "Upgrade" or "Repair Now" button.
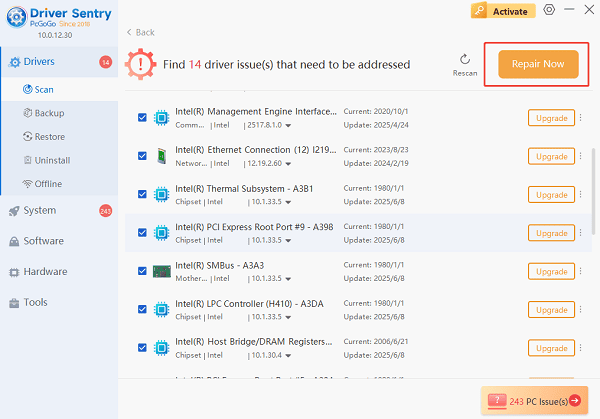
Driver Sentry will download the latest, certified versions for your specific hardware.
Finalize:
After the installation is complete, restart your computer. A fresh set of stable drivers often resolves sound loss immediately.
Method 2: Roll Back or Reinstall the Audio Driver
If the sound failure occurred immediately after a Windows update, the new driver may be the source of the problem.
1). Press Windows Key + X and select "Device Manager".
2). Expand the "Sound, video and game controllers" category.
3). Right-click on your audio device (e.g., Realtek Audio) and select "Properties".
4). Go to the "Driver" tab.
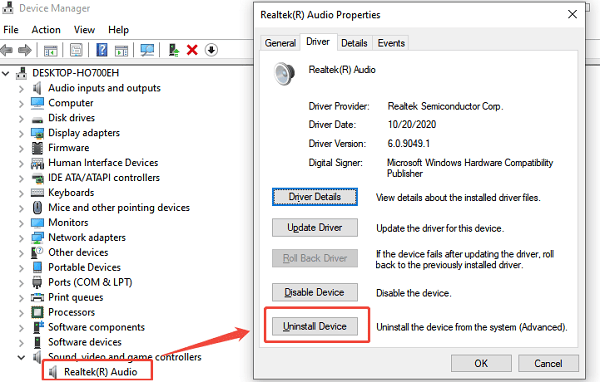
Roll Back: If the "Roll Back Driver" button is available, click it. This reverts to the previous working driver.
Reinstall: If the button is unavailable, select "Uninstall device". Check the box to "Attempt to remove the driver software for this device", and then restart your PC. Windows will automatically attempt to reinstall a basic functional driver upon reboot.
Part II: Connection and System Checks
These steps rule out basic mistakes and ensure Windows audio services are running correctly.
Method 1: Check Connections and Volume Mixer
Simple physical disconnections and muted software settings are common culprits.
Physical Connections: Ensure speakers or headphones are securely plugged into the correct green audio jack (for desktop PCs) or the correct port (for laptops). If using USB or HDMI audio, try a different port.
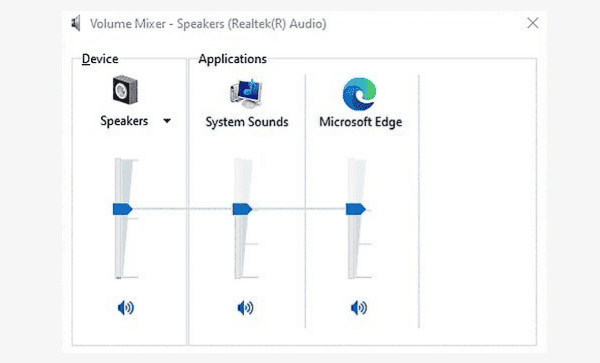
Volume Mixer: Right-click the Speaker icon in the taskbar and select "Open Volume Mixer". Ensure that the main volume slider, as well as the volume sliders for all applications, are turned up and not muted.
Check Playback Device: Right-click the Speaker icon and select "Sounds". In the "Playback" tab, ensure your active speaker/headphone device is set as the "Default Device" and is not disabled.
Method 2: Ensure Windows Audio Services Are Running
Critical Windows services must be active for any sound output.
Press Windows Key + R, type "services.msc", and press Enter.
In the Services window, scroll down and find the "Windows Audio" service.
Right-click the service and select "Properties".
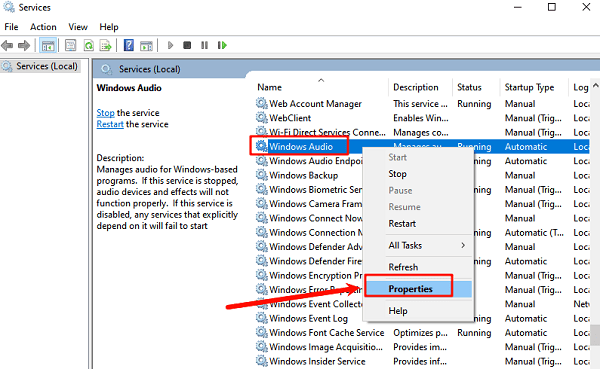
Ensure the Startup Type is set to "Automatic".
If the service is not running, click the "Start" button under the Service status. Repeat this process for the "Windows Audio Endpoint Builder" service.
Part III: Advanced Troubleshooting
If the above methods fail, the issue may require more specialized system checks.
Disable Audio Enhancements
Some audio driver enhancements can conflict with Windows, causing sound to drop out entirely.
Right-click the Speaker icon in the taskbar and select "Sounds".
In the "Playback" tab, right-click your default speaker/headphone device and select "Properties".
Go to the "Enhancements" or "Advanced" tab.
Check the box that says "Disable all sound effects" or try changing the Default Format to a lower quality setting (e.g., 16 bit, 44100 Hz).
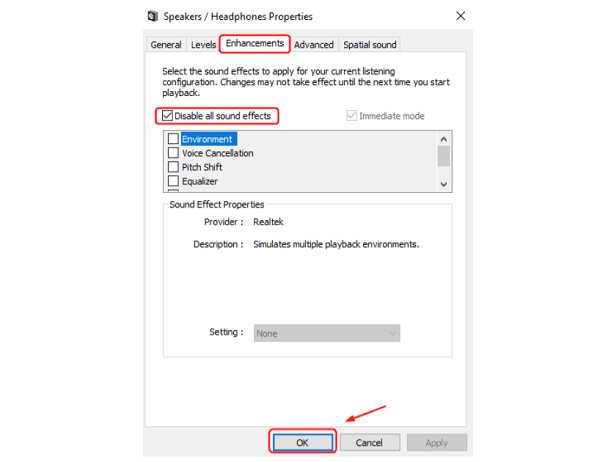
Click "Apply" and test the sound.
Conclusion
Loss of sound on a computer is a frustrating but usually fixable issue rooted in driver or configuration errors. The most effective way to address the problem is to update drivers with Driver Sentry.
By systematically checking your Volume Mixer, physical connections, and the status of the Windows Audio services, you can quickly isolate the fault and restore full sound output to your system.